Using the Google AlloyDB Destination Component
The Google AlloyDB Destination Component can be used to write to a Destination table in a Google AlloyDB instance. The component includes four pages:
- General
- Columns
- Pre & Post Commands
- Error Handling
General Page
The General page of the Google AlloyDB Destination Component allows you to specify the general settings of the component.
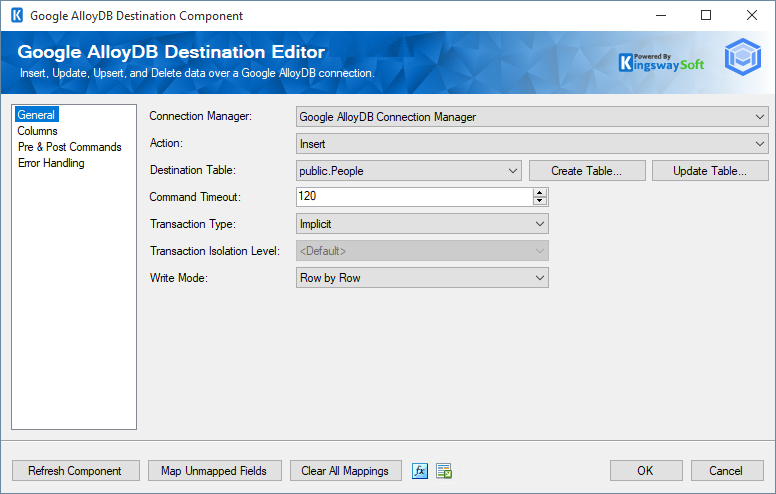
- Connection Manager
-
The Google AlloyDB Destination component requires a connection to connect to the instance. The Connection Manager drop-down will show a list of all Google AlloyDB connection managers that are available for your current SSIS package.
- Action
-
The action or command you want to execute on the Destination Table. Available actions include:
- Insert: Add records to the Destination Table.
- Update: Update existing records in the Destination Table.
- Upsert: If the specified record exists in the Destination Table it is updated otherwise, it is inserted.
- Delete: Delete existing records from the Destination Table.
- Custom Command: A custom command like a procedure can be specified in the provided space.
- Destination Table
-
The Destination Table drop-down displays a list of available tables for the instance specified in the Connection Manager.
- Create Table
-
Opens the Google AlloyDB Table Creator show below:
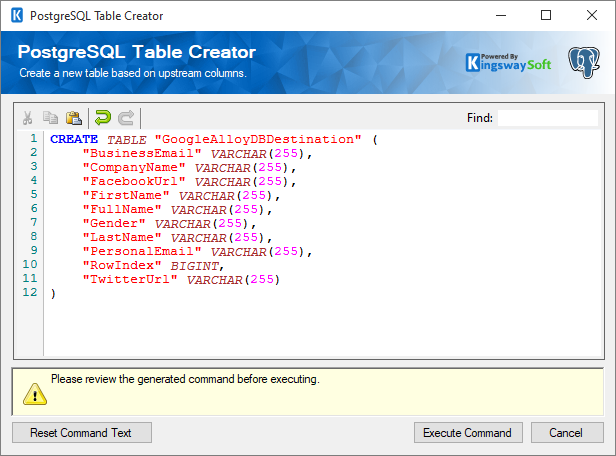
It auto-generates a command based on the selected Connection Manager and Input Columns to create a new table. You can further customize the command to suit your needs and then click the 'Execute Command' button. The table you created will be selected in the Destination Table property.
- Command Timeout
-
The Command Timeout option allows you to specify the number of seconds for the command timeout values. The default value is 120 seconds.
- Transaction Type
-
This option allows you to specify the type of transactions by choosing Explicit and selecting an Isolation Level or by choosing Implicit.
- Transaction Isolation Level (When Transaction Type is chosen as Explicit)
-
The Transaction Isolation Level option allows you to specify concurrency behaviors. The below options are available.
- Chaos
- Read Committed
- Read Uncommitted
- Repeatable Read
- Serializable
- Snapshot
- Write Mode
-
There are three write modes from which you can select.
- Row by Row
- Batch (for improved performance)
- Bulk (recommended for the best performance)
- Upsert Mode (Only for Upsert action since v25.1)
-
The Upsert Mode option allows you to specify how the data is written while performing an Upsert action. There are a total of three options available:
- Full Upsert
- Insert Only - Existing records are ignored
- Update Only - New records are ignored
- Only Update First Match (Available for Update and Upsert option)
-
This option can be enabled to update only the first match.
- Prevent Null Overwrites (Available for Update and Upsert option)
-
This option can be enabled to prevent Null overwrites.
- Fail On No Affected Records (since v23.1)
-
The Fail On No Affected Records option allows you to toggle between whether fail or not when there are no affected records for that action. This option is only available for Update and Delete actions when the above Row by Row writing mode is used. This option is enabled by default when applicable (if Update or Delete action is used for row-by-row writing). It is a feature designed to ensure that the incoming rows should always find a matching records in the target system for the write operation. The option can be disabled when such assurance is not needed.
- Only Delete First Match (Available for Delete action)
-
This option can be enabled to delete only the first match.
Columns Page
The Columns page of the Google AlloyDB Destination Component allows you to map the columns from upstream components to fields of the specified Destination Table in the General Page. The Columns Page is not available when the selected action is Custom Command.
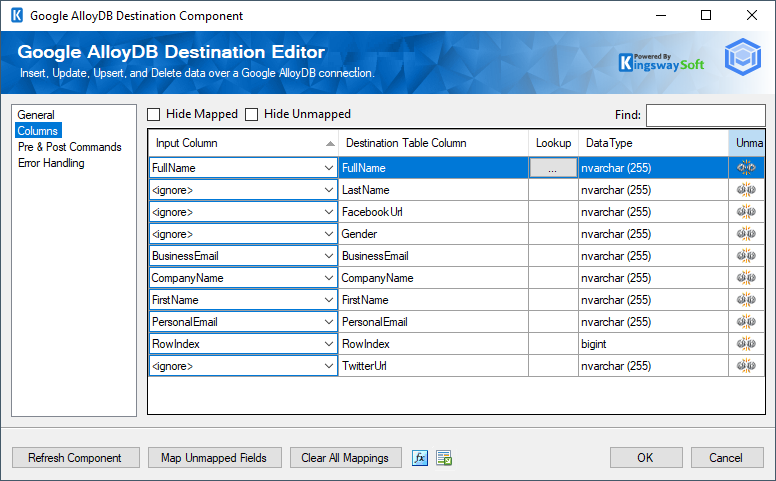
- Input Column: Select an Input Column from an upstream component here.
- Destination Table Column: This is the field you are writing data to.
- Lookup: Enable the lookup feature by mapping the virtual '<Lookup>' input column to the destination table column. When this option is selected, the component can perform a lookup based on input values. For further information about how to use the Lookup feature, please refer to the Working with the Lookup Feature section below.
- Data Type: This column indicates the type of value for the current field.
- Unmap: This column can be used to unmap the field from the upstream input column, or otherwise, it can be used to map the field to an upstream input column by matching its name if the field is not currently mapped.
Working with the Lookup Feature
The Lookup feature allows you to perform a lookup based on the input values. To configure the Lookup feature, you map the destination table column with the virtual '<Lookup>' input column. You will be presented with the following screen.
- Target Table
-
The Target Table is a read-only property that shows the destination table configured in the Google AlloyDB Destination Component.
- Target Column
-
The Target Column is a read-only property that shows the target column which is configured to use the Lookup feature.
- Lookup Table
-
Select the Lookup Table from the drop-down list that displays available tables for the database specified in the Connection Manager.
- Returning Column
-
Select the Returning Column from the drop-down list that displays available columns for the specified Lookup Table.
- Default Value
-
When the Default Value is specified, the component will use this default value to write to the target column should the input value lookup fail
- Lookup Condition
-
- + sign: Add lookup condition.
- - sign: Remove lookup condition.
- Arrows: Use arrows to group the lookup conditions.
- AND/OR: Specify AND or OR to create logical expressions of your lookup conditions.
- Lookup Column: Select the lookup column from the drop-down list which displays available columns for the specified Lookup Table.
-
Operator: Use the query operator to specify how each input value in a clause must relate to the corresponding value in a lookup table.
- =: the value of the field is equal to the selected lookup value
- <>: the value of the field is not equal to the selected lookup value
- >: the value of the field is greater than the selected lookup value
- <: the value of the field is less than the selected lookup value
- >=: the value of the field is greater than or equal to the selected lookup value
- <=: the value of the field is less than or equal to the selected lookup value
-
LIKE: the value of the field is equal to the selected lookup value based on pattern match, supports %, _, [ ], and [^] wildcards
- Note: This option may impact performance, consider using = whenever possible.
-
NOT LIKE: the value of the field is not equal to the selected lookup value based on pattern match, supports %, _, [ ], and [^] wildcards
- Note: This option may impact performance, consider using <> whenever possible.
- BETWEEN: the value of the field is between the values of two selected lookup values
- IS NULL: the value of the field is NULL
- IS NOT NULL: the value of the field is not NULL
-
Input Value: The Input Value for the lookup condition. Available options are:
- Input Column
- Enables user to perform Lookup match by selecting a field from the Lookup Table Column
- Variable
- Enables user to perform Lookup match based on a System or User SSIS variable
- Static Value
- Enables user to perform Lookup match based on a static value
- Input Column
Pre & Post Commands Page
The Pre & Post Commands page allows you to specify commands you wish to execute before and after component execution
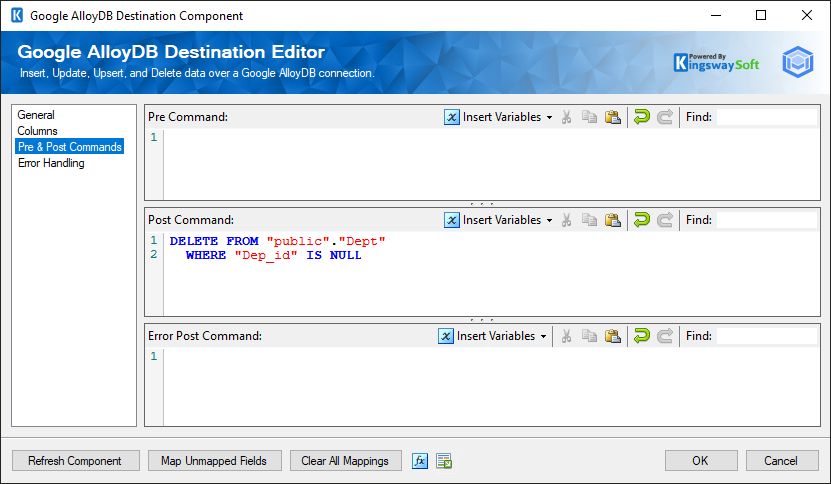
- Pre Command
-
The Pre Command will be executed in the pre-execute phase. Leave blank to NOT execute any command.
- Success Post Command (Since v23.1)
-
The Success Post Command will be executed in the post-execute phase when it succeeds. Leave it blank if you do not want to execute any command.
- Error Post Command (Since v23.1)
-
The Error Post Command will be executed in the post-execute phase when an error takes place. Leave blank to NOT execute any command.
Error Handling Page
The Error Handling page allows you to specify how errors should be handled when they happen.
There are three options available.
- Fail on error
- Redirect rows to error output
- Ignore error
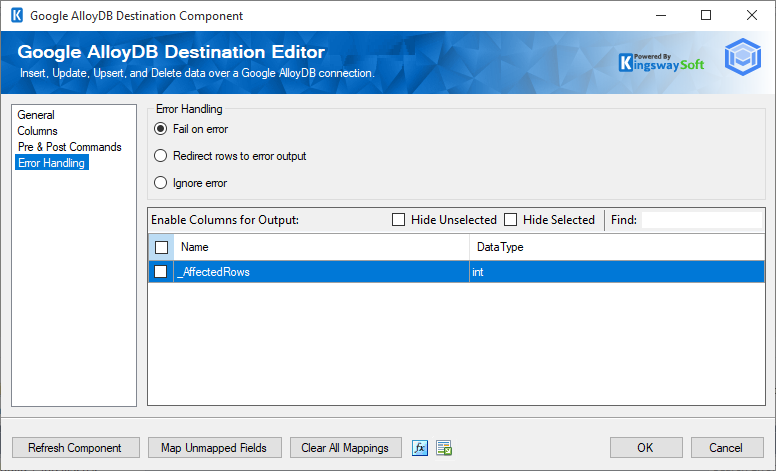
When the Redirect rows to error output option is selected, rows that failed to be sent will be redirected to the 'Error Output' output of the Transformation Component. As indicated in the screenshot below, the blue output connection represents rows that were successfully sent, and the red 'Error Output' connection represents rows that were erroneous. The 'ErrorMessage' output column found in the 'Error Output' may contain the error message that was reported by the server or the component itself.
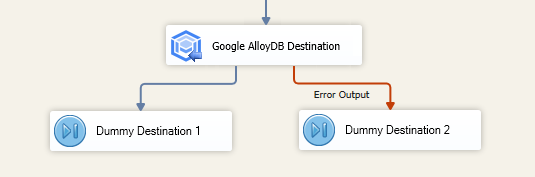
In the Error Handling page, there are also options that can be used to enable or disable the following output fields for the destination component's Default Output.
_AffectedRows: Reports the number of affected rows for the SQL script executed for each incoming row. This option is not available when the Bulk mode is used.
