Adobe Commerce/Magento
Building the JDBC URL
After installing the license, access the connection management page by executing the command java -jar kingswaysoft.jdbc.jar. Enter the necessary details, and the program will automatically generate the JDBC connection URL. Users can click Test Connection to test the generated URL and Copy to Clipboard to copy the connection string for use within the application where the JDBC driver is being used.
Note: If the license is not installed, you can still use the connection manager to generate a JDBC URL; however, the 'Test Connection' feature will be disabled.
General Page
The General page allows you to specify connection properties and login credentials for the Magento / Adobe Commerce REST service:
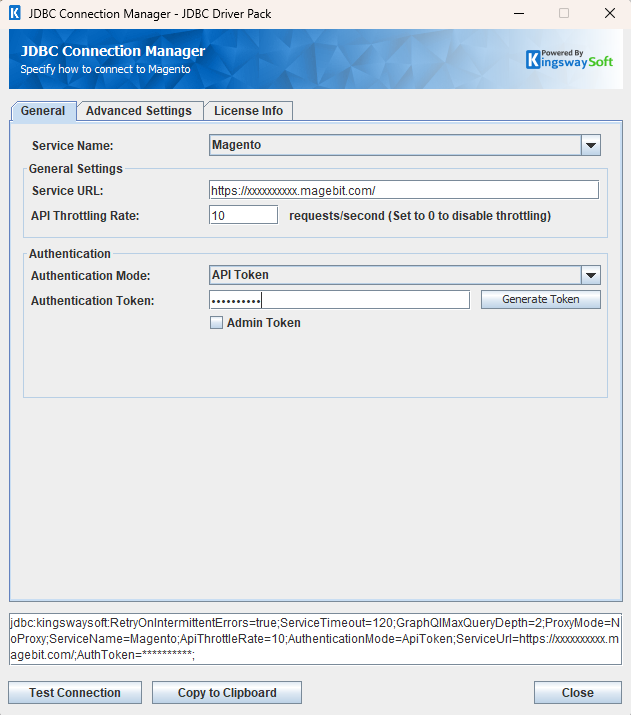
- General Settings
-
- Service URL
-
The full URL of the Magento / Adobe Commerce instance that will be connected to.
- API Throttling Rate
-
The API Throttling Rate option will limit the number of requests that can be sent per second. Set this value to 0 to disable API throttling.
- Authentication
-
- Authentication Mode
-
The Authentication Mode option allows you to choose the method used to authenticate with the API. Available options are:
- API Token
- OAuth
Authentication Methods for Adobe Commerce/Magento
API Token
A pre-existing token can be used to establish a connection. If you wish to generate a new authentication token, click **Generate Token** to go through the token generation process. You can use the generated access token to connect.
- Authentication Token
-
If you have an authentication token that you would like to use, enter it in the authentication field, and check the 'Admin Token' checkbox if it is an Admin token. If it is a customer token do not check the box. If you do not have a Magento / Adobe Commerce token you can generate one by clicking the Generate Token button.
- Generate Token
-
If you click the Generate Token button the 'Generate Token' dialog will appear. You can enter credentials for a Magento / Adobe Commerce user, and then generate an admin token, or a customer token depending on what kind of user you use to access Magento / Adobe Commerce. The generated token will automatically populate the 'Authentication Token' field and check the 'Admin Token' checkbox as appropriate. Credentials entered in this dialog are not saved, they are just used to generate a token and then discarded.
OAuth
Users can choose to establish a connection using their consumer key, consumer secret, access token, and access token secret. This will generate a token using the signature method HMAC-SHA1.
- Consumer Key
-
This field allows you to input the Consumer Key linked to your Magento/Adobe Commerce instance.
- Consumer Secret
-
This field allows you to input the Consumer Secret linked to your Magento/Adobe Commerce instance.
- Access Token
-
This field allows you to input the Access Token linked to your Magento/Adobe Commerce instance.
- Access Token Secret
-
This field allows you to input the Access Token Secret linked to your Magento/Adobe Commerce instance.
After all the connection information has been provided, click the "Test Connection" button to test if the user credentials entered can successfully connect to the selected service.
Advanced Settings Page
The Advanced Settings page allows you to specify advanced settings for the connection.
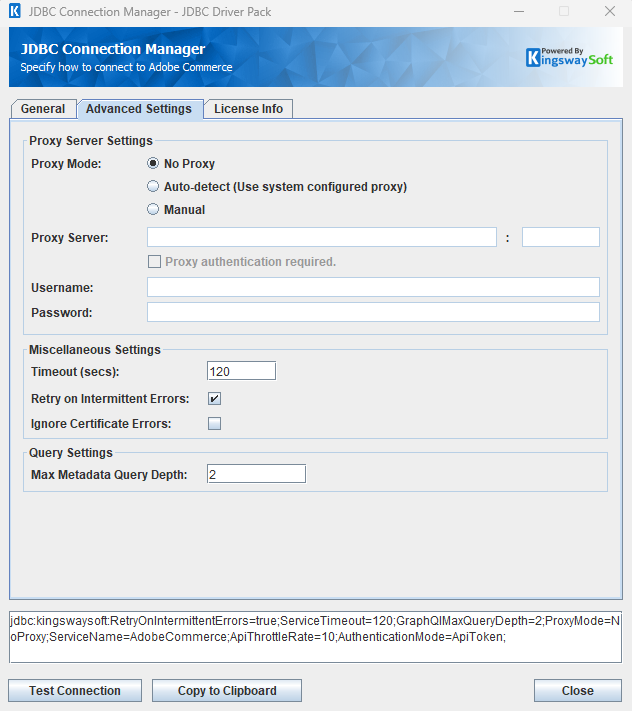
- Proxy Mode
-
The Proxy Mode option allows you to specify how you want to configure the proxy server setting. There are three options available.
- No Proxy
- Auto-detect (Use system configured proxy)
- Manual
- Proxy Server
-
Using the Proxy Server option allows you to specify the name of the proxy server for the connection.
- Port
-
The Port option allows you to specify the port number of the proxy server for the connection.
- Username (Proxy Server Authentication)
-
The Username option (under Proxy Server Authentication) allows you to specify the proxy user account.
- Password (Proxy Server Authentication)
-
The Password option (under Proxy Server Authentication) allows you to specify the proxy user's password.
- Timeout (secs)
-
The Timeout (secs) option allows you to specify a timeout value in seconds for the connection. The default value is 120 seconds. Specify 0 for infinite timeout.
- Retry on Intermittent Errors
-
The retry on intermittent errors determines if requests will be retried when there is an error. If this option is checked requests will be retried up to 3 times.
- Ignore Certificate Errors
-
This option can be used to ignore those SSL certificate errors when connecting to the target server.
Warning: Enabling the "Ignore Certificate Errors" option is generally NOT recommended, particularly for production instances. Unless there is a strong reason to believe the connection is secure - such as the network communication is only happening in an internal infrastructure, this option should be unchecked for best security.
Note: When this option is enabled, it applies to all HTTP-based SSL connections in the same job process.
- Concurrent Writing Threads
-
This option can be used to set the number of threads to be used during write operations. This can improve performance during large-volume write operations.
- Max Metadata Query Depth
-
The Max Metadata Query Depth option allows you to specify how deep you would like to go to discover the metadata fields.
Using the JDBC Driver
Explore detailed examples in this section that demonstrate the application of JDBC classes such as Connection, Statement, and ResultSet to effectively manage interactions with Magento data. This section covers the use of regular statements and prepared statements for executing complex or frequently executed queries.
Executing Statements
Once you've connected from your code (see Connecting with DriverManager and Connecting with DataSource), you can execute SQL statements using the Statement class. Refer to the Executing Prepared Statements section for information on how to execute parameterized statements.
SELECT
Use the Statement class's generic execute method or the executeQuery method to execute SQL statements that return data. To retrieve the results of a query, you would then call the getResultSet method of the Statement.
String sql = "SELECT * FROM products WHERE search = 'pants'"; try { ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); LOGGER.info(resultSet.toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.toString()); }
INSERT
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute an INSERT operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the inserted data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer (input-email, input-firstname, input-lastname) VALUES ('[email protected]', 'First', 'Last')"; try { statement.executeUpdate(sql); LOGGER.info(statement.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.toString()); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":{"email":"[email protected]","firstname":"First","lastname":"Last"}},false
UPDATE
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute an UPDATE operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the updated data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "UPDATE customer SET input-firstname = 'updateFirst' WHERE input-email = '[email protected]'"; try { statement.executeUpdate(sql); LOGGER.info(statement.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.toString()); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":{"email":"[email protected]","firstname":"updateFirst"}},false
DELETE
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute a DELETE operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the deleted data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "DELETE FROM customerAddress WHERE id = '1'"; try { statement.executeUpdate(sql); LOGGER.info(statement.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.toString()); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":1},false
CallMutation
You can use either the generic execute method or the executeQuery method of the Statement class to execute mutations through a "CallMutation" query. CallMutation statements are formatted similarly to Insert statements but require the full mutation name. The field to output can be specified using an OUT parameter located in the columns list prefixed by "OUT". If the mutation has fields to return (see system.functions and system.functions.columns), an OUT parameter is required.
For example, the corresponding CallMutation Statement for INSERT INTO customer (input-email) VALUES ('email') is CallMutation customerCreate (input-email, OUT customer-email) VALUES ('email').
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the mutation data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "CallMutation reorderItems (orderNumber, OUT cart-id) VALUES ('001')"; try { statement.executeUpdate(sql); LOGGER.info(statement.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.toString()); }
cart-id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror KxQWbJLzjFhR9pLZl1KShdV2zXyVuV7Q,null,null,{"var1":"001"},false
Executing Prepared Statements
Using a PreparedStatement can improve performance when you need to execute a SQL statement multiple times with different parameters. Unlike a Statement object, a PreparedStatement object is provided with a SQL statement when it is created, which can then be executed with different values each time. This special type of statement is derived from the more general class, Statement.
Below are the steps outlining how to execute a prepared statement:
- Create a PreparedStatement: Use the prepareStatement method of the Connection class to instantiate a PreparedStatement. Refer to Connecting with DriverManager or Connecting with DataSource for information related to establishing connections.
- Set Parameters: Declare parameters by calling the corresponding setter method of the PreparedStatement. Note: The parameter indices start at 1.
- Execute the Statement: Use the generic execute or executeUpdate method of the PreparedStatement.
- Retrieve Results: Call the getResultSet method of the Prepared Statement to obtain the query results, which will be returned as a ResultSet.
- Iterate Over the Result Set: Use the next method of the ResultSet to iterate through the results. To obtain column information, utilize the ResultSetMetaData class. Instantiate a ResultSetMetaData object by calling the getMetaData method of the ResultSet.
SELECT
Use the Statement class's generic execute method or the executeQuery method to execute SQL statements that return data.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the retrieved data.
String sql = "SELECT * FROM products WHERE search = ?"; try { PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "pants"); ps.execute(sql); while (ps.getResultSet().next()) { for (int i = 1; i <= ps.getResultSet().getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) { LOGGER.info(ps.getResultSet().getMetaData().getColumnLabel(i) + "=" + ps.getResultSet().getString(i)); } } } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.error(e); }
INSERT
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute an INSERT operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. Users can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the ID of inserted data, exceptions raised during execution, and the data affected by the insertion.
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer (input-email, input-firstname, input-lastname) VALUES (?, ?, ?)"; try { PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "[email protected]"); ps.setString(2, "First"); ps.setString(3, "Last"); ps.executeUpdate(); LOGGER.info(ps.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.error(e); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":{"email":"[email protected]","firstname":"First","lastname":"Last"}},false
UPDATE
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute an UPDATE operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. Users can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the ID of updated data, exceptions raised during execution, and the data affected by the update.
String sql = "UPDATE customer SET input-firstname=? WHERE input-email = ?"; try { PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "updateFirst"); ps.setString(2, "[email protected]"); ps.executeUpdate(); LOGGER.info(ps.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.error(e); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":{"email":"[email protected]","firstname":"updateFirst"}},false
DELETE
Use either the generic execute method or the executeUpdate method of the Statement class to execute a DELETE operation.
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the deleted data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "DELETE FROM customerAddress WHERE id = ?"; try { PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, "1"); ps.executeUpdate(); LOGGER.info(ps.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.error(e); }
id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror null,null,null,{"var1":1},false
CallMutation
You can use either the generic execute method or the executeQuery method of the Statement class to execute mutations through a "CallMutation" query. CallMutation statements are formatted similarly to Insert statements but require the full mutation name. The field to output can be specified using an OUT parameter located in the columns list prefixed by "OUT". If the mutation has fields to return (see system.functions and system.functions.columns), an OUT parameter is required.
For example, the corresponding CallMutation Statement for INSERT INTO customer (input-email) VALUES ('email') is CallMutation customerCreate (input-email, OUT customer-email) VALUES ('email').
The results of SQL queries are saved in a ResultSet. You can retrieve the ResultSet after execution to view the mutation data's ID, exceptions raised during execution, and details of the affected data.
String sql = "CallMutation reorderItems (orderNumber, OUT cart-id) VALUES (?)"; try { Connection connection = buildRestConnectionFromDriverManager(); PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(customSql); ps.setString(1, "001"); ps.executeUpdate(); LOGGER.info(ps.getResultSet().toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
cart-id,errorcode,errormessage,processdata,haserror KxQWbJLzjFhR9pLZl1KShdV2zXyVuV7Q,null,null,{"var1":"001"},false
Metadata Discovery
This section provides examples on how to retrieve table and column metadata using the getTables, getColumns, and getPrimaryKeys methods from the DatabaseMetaData interface. These are essential for discovering database structures.
Tables
The getTables method from the DatabaseMetaData interface can be used to retrieve a list of tables.
This method only retrieves tables that are not write-only.
To get a list of tables which include write-only tables, query the table [system.tables](/products/jdbc-driver-pack/help-manual/advancedfeatures#systemtables).
try { Connection connection = buildRestConnectionFromDriverManager(); ResultSet rs = connection.getMetaData().getTables(null, null, null, null); LOGGER.info("\r\n" + rs.toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.getMessage()); }
TABLE_CAT,TABLE_SCHEM,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,REMARKS null,null,adaptive_auth_event,Table, null,null,agent_assist_recommendation,Table, null,null,agent_file,Table, ......
The getTables method returns the following metadata columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CAT | String | The catalog that contains the table. |
| TABLE_SCHEM | String | The schema of the table. |
| TABLE_NAME | String | The name of the table name. |
| TABLE_TYPE | String | The type of the table (e.g., TABLE or VIEW). |
| REMARKS | String | An optional description of the table. |
Columns
Use the getColumns method of the DatabaseMetaData interface to retrieve detailed information about database columns. To narrow the results to a specific table, specify the table name using the parameter table_name.
This method returns columns only for tables that are not write-only.
To get columns for tables which are write-only, query the table [system.columns](/products/jdbc-driver-pack/help-manual/advancedfeatures#systemcolumns).
try { Connection connection = buildRestConnectionFromDriverManager(); ResultSet rs = connection.getMetaData().getColumns(null, null, "agent_file", null); LOGGER.info(rs.toString()); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
TABLE_CAT,TABLE_SCHEM,TABLE_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,DATA_TYPE,TYPE_NAME,COLUMN_SIZE,BUFFER_LENGTH,DECIMAL_DIGITS,NUM_PREC_RADIX,NULLABLE,REMARKS,COLUMN_DEF,SQL_DATA_TYPE,SQL_DATETIME_SUB,CHAR_OCTET_LENGTH,ORDINAL_POSITION,IS_NULLABLE,IS_AUTOINCREMENT,IS_GENERATEDCOLUMN,DTS_TYPE null,null,agent_file,sys_updated_on,91,java.util.Date,40,null,0,0,null,null,null,91,null,null,null,null,null,null,DT_DBDATE null,null,agent_file,start_date,91,java.util.Date,40,null,0,0,null,null,null,91,null,null,null,null,null,null,DT_DBDATE null,null,agent_file,sys_updated_by,12,java.lang.String,40,null,0,0,null,null,null,12,null,null,null,null,null,null,DT_WSTR
The getColumns method returns the following columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CAT | String | The database name. |
| TABLE_SCHEM | String | The table schema. |
| TABLE_NAME | String | The table name. |
| COLUMN_NAME | String | The column name. |
| DATA_TYPE | Integer | The data type represented by a constant value from java.sql.Types. |
| TYPE_NAME | String | The data type name used by the driver. |
| COLUMN_SIZE | Integer | The length in characters of the column or the numeric precision. |
| BUFFER_LENGTH | Integer | The buffer length. |
| DECIMAL_DIGITS | Integer | The column scale or number of digits to the right of the decimal point. |
| NUM_PREC_RADIX | Integer | The radix, or base. |
| NULLABLE | Integer | Whether the column can contain null as defined by the following JDBC DatabaseMetaData constants: columnNoNulls (0) or columnNullable (1). |
| REMARKS | String | The comment or note associated with the object. |
| COLUMN_DEF | String | The default value for the column. |
| SQL_DATA_TYPE | Integer | Reserved by the specification. |
| SQL_DATETIME_SUB | Integer | Reserved by the specification. |
| CHAR_OCTET_LENGTH | Integer | The maximum length of binary and character-based columns. |
| ORDINAL_POSITION | Integer | The position of the column in the table, starting at 1. |
| IS_NULLABLE | String | Whether a null value is allowed: YES or NO. |
| IS_AUTOINCREMENT | String | Whether the column value is assigned by Magento in fixed increments. |
| IS_GENERATEDCOLUMN | String | Whether the column is generated: YES or NO. |
| DTS_TYPE | String | Object DTS attribute type. |
Primary Keys
The getPrimaryKeys method in the DatabaseMetaData interface is used to retrieve metadata about primary keys for a given table in Magento.
try { Connection connection = buildRestConnectionFromDriverManager(); ResultSet resultSet = connection.getMetaData().getPrimaryKeys(null, null, "cart"); LOGGER.info("\r\n" + resultSet.toString()); Assertions.assertNotNull(resultSet); } catch (SQLException e) { LOGGER.severe(e.getMessage()); }
TABLE_NAME,PRIMARY_COLUMN_NAME cart,id
The getPrimaryKeys method returns the following columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_NAME | String | The name of the table that contains the primary key. |
| PRIMARY_COLUMN_NAME | String | The name of the column that serves as the primary key for the table. |
Connection Settings
| Connection Setting | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AccessToken | String | "" | The AccessToken is used to authenticate access to Magento. |
| AccessTokenSecret | String | "" | The AccessTokenSecret is a secret key associated with the AccessToken. |
| ApiThrottleRate | Integer | 10 | The maximum number of API requests a client can make to the server within a specific time period, defined in the ThrottleRateUnit setting. |
| AuthenticationMode | String | "ApiToken" | AuthenticationMode specifies the method used to authenticate when connecting to Magento GraphQL API. |
| AuthToken | String | "" | The AuthToken is a token provided by Magento that acts a a form of authentication for access. |
| CacheExpirationTime | Integer | 30 | Defines the expiration time for cache. A value of 0 disables caching. |
| ConcurrentWritingThreads | Integer | 1 | The number of threads for executing operations in parallel. A value of 0 will disable multi threading. |
| ConnectionTimeout | Integer | 30 | ConnectionTimeout is the maximum amount of time the program will wait to set up a connection to the Magento API. |
| ConsumerKey | String | "" | The ConsumerKey is a public identifier for the client application that is requesting access to the service. |
| ConsumerSecret | String | "" | The ConsumerSecret is a private key that pairs with the ConsumerKey. |
| GraphQlMaxQueryDepth | Integer | 2 | GraphQlMaxQueryDepth refers to the maximum depth allowed for a GraphQL query to avoid performance issues. It has a maximum valid value of 8 and will be used when a higher depth is used. |
| IgnoreCertificateErrors | Boolean | false | Specifies whether to verify the certificate when connecting to Magento. If certificate verification is not required, you can set this value to 'true'. |
| IgnoreError | Boolean | false | Determines if the program continues executing SQL statements after encountering an error. |
| IsAdminToken | Boolean | false | Specifies whether the token has administrative privileges or permissions. |
| LogFileSize | String | "10485760" | A string specifying the maximum size in bytes for a log file. |
| LogLevel | String | "INFO" | The logging level for the JDBC driver. |
| LogPath | String | "./jdbcLogs" | The directory where log files are stored. |
| OemKey | String | "" | The OEM license key. |
| ProxyMode | String | NoProxy | This setting configures the proxy. Allowed values are "NoProxy", "AutoDetect" and "Manual". |
| ProxyPassword | String | "" | The password to be used to authenticate to the proxy. |
| ProxyServer | String | "" | The host of the proxy server. |
| ProxyServerPort | Integer | 0 | The port of the proxy server. |
| ProxyUsername | String | "" | The username to be used to authenticate to the proxy. |
| ReadBatchSize | Integer | 1000 | ReadBatchSize is used to set how many records can be read from Magento in a single call. |
| ResultPath | String | "" | The path where the execution result files are saved. |
| RetryOnIntermittentErrors | Boolean | true | The RetryOnIntermittentErrors parameter indicates whether to retry the connection when it might occasionally fail due to temporary issues. |
| SaveResult | Boolean | false | The SaveResult parameter indicates whether to save the execution results to a file. |
| ServiceName | String | "" | The ServiceName refers to the name of the service API selected by the user. |
| ServiceTimeout | Integer | 120 | The ServiceTimeout is the timeout to receive the full response from Magento API. |
| ServiceUrl | String | "" | The ServiceUrl is the instance URL used for connecting to Magento. |
| Suppress404NotFoundError | Boolean | true | When set to true, if a query results in an HTTP 404 error, a result set will still be created. When set to false, an error is logged instead and no result set is created. |
| ThrottleRateUnit | String | "PerSecond" | The unit of time for limiting API requests to avoid being throttled. Valid values include, "PerSecond", "PerMinute" and "PerHour". |
| WriteBatchSize | Integer | 200 | WriteBatchSize is used to set how many records can be written to Magento in a single call. |

